Case Number : Case 579 - 28 Aug Posted By: Guest
Please read the clinical history and view the images by clicking on them before you proffer your diagnosis.
Submitted Date :
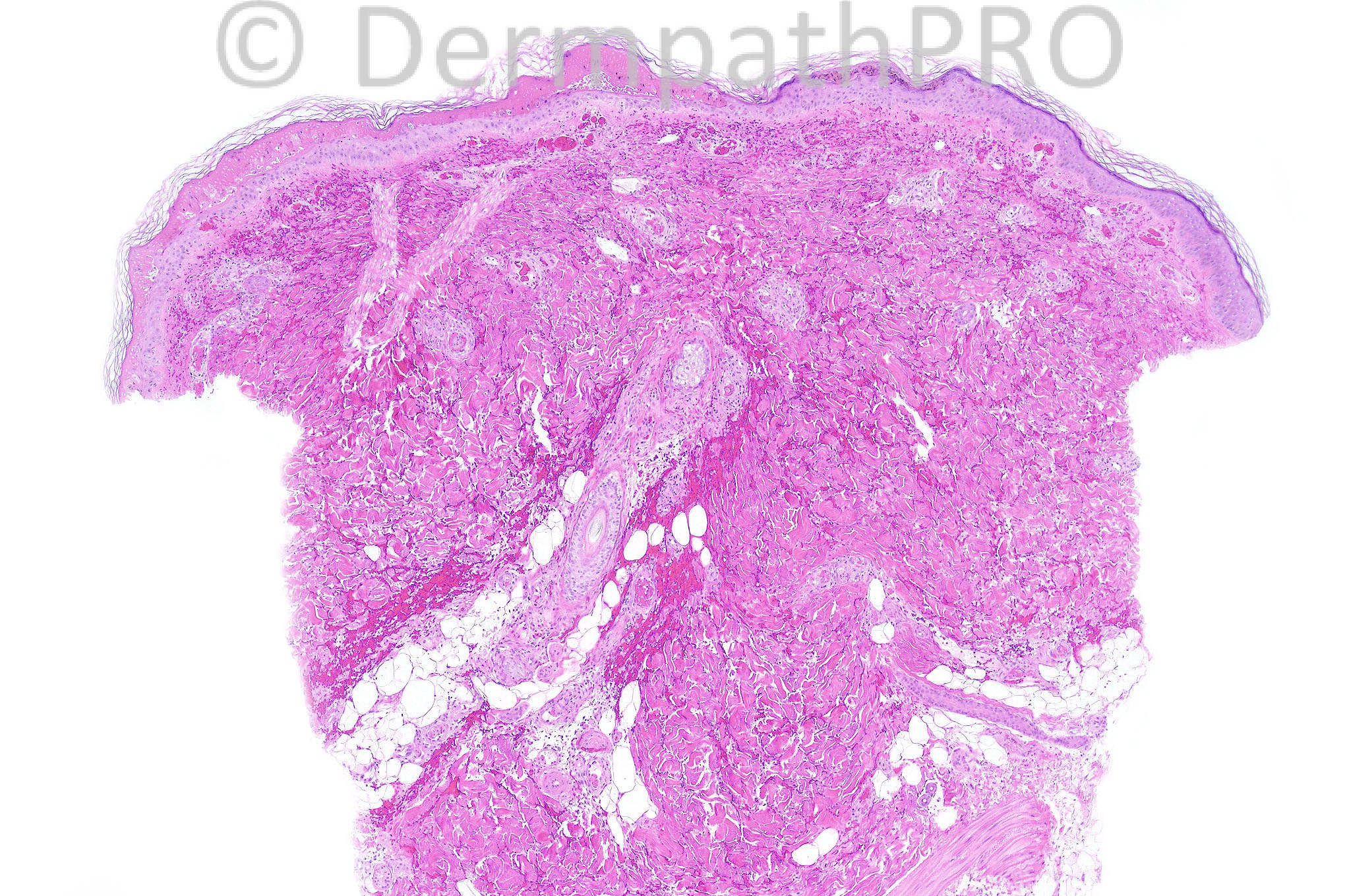
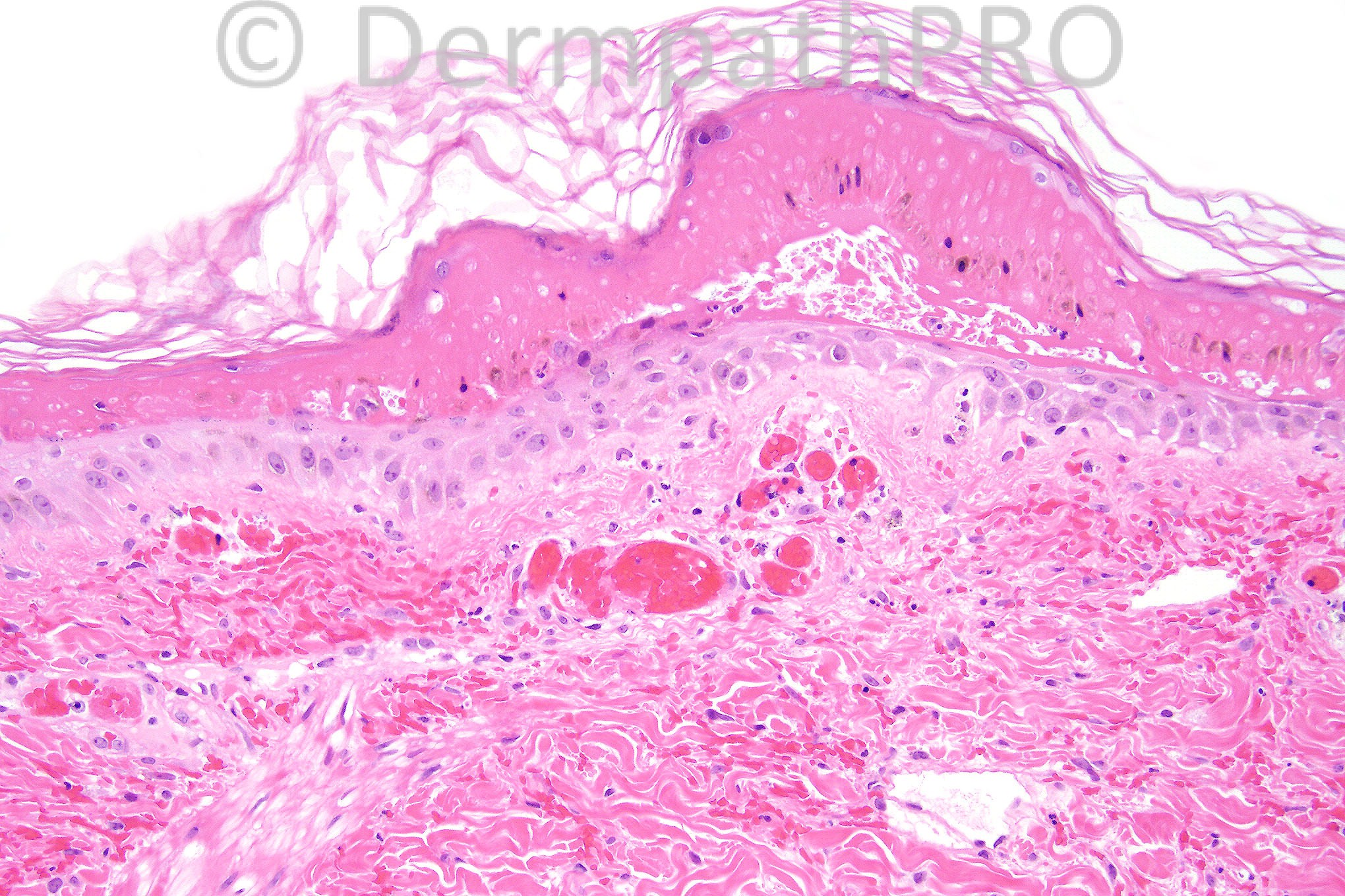
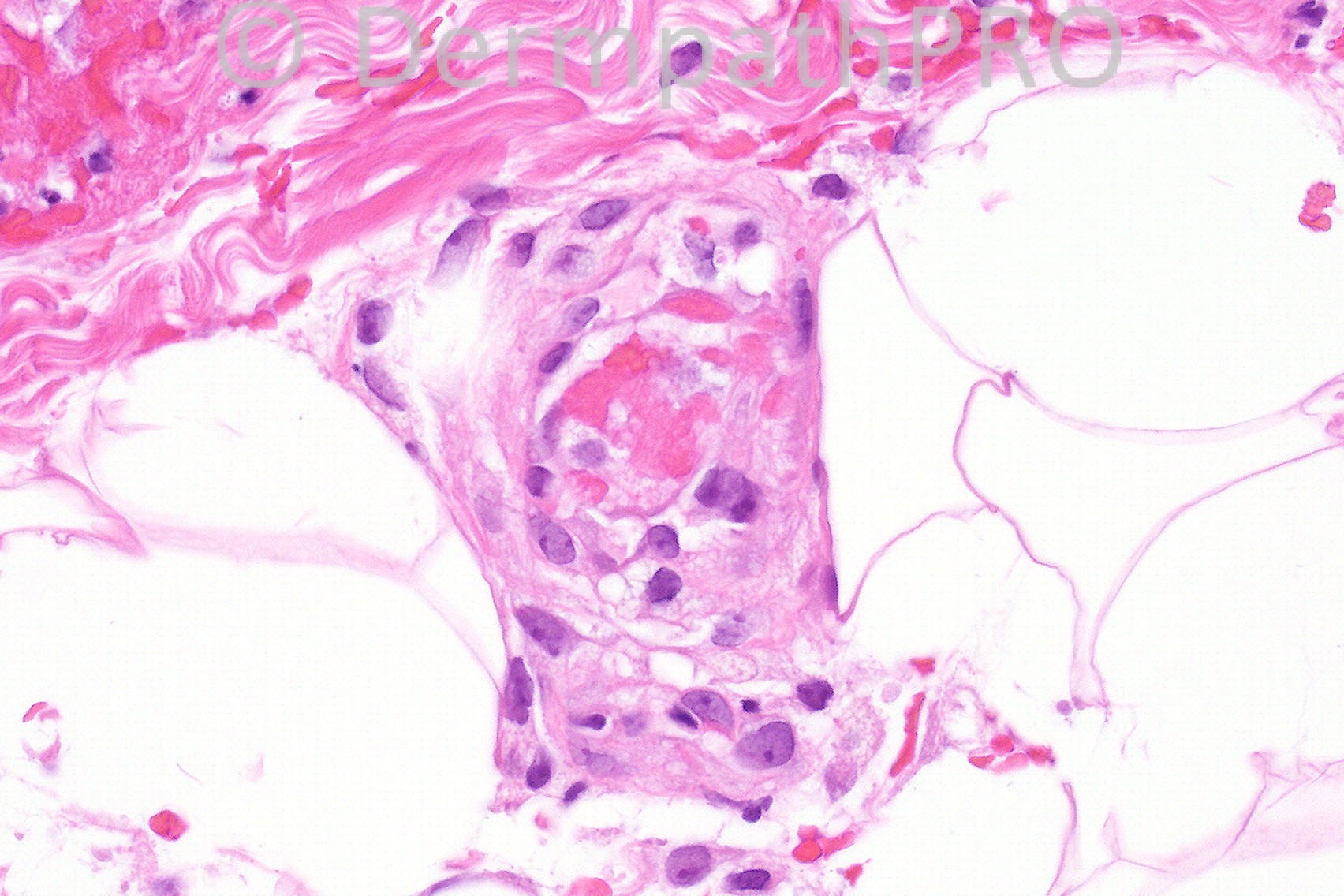
Female aged 28 years with widespread purpuric lesions clinically thought to represent polyarteritis nodosa or Wegener's granulomatosis.


User Feedback