Case Number : Case 603 - 1 Oct Posted By: Guest
Please read the clinical history and view the images by clicking on them before you proffer your diagnosis.
Submitted Date :
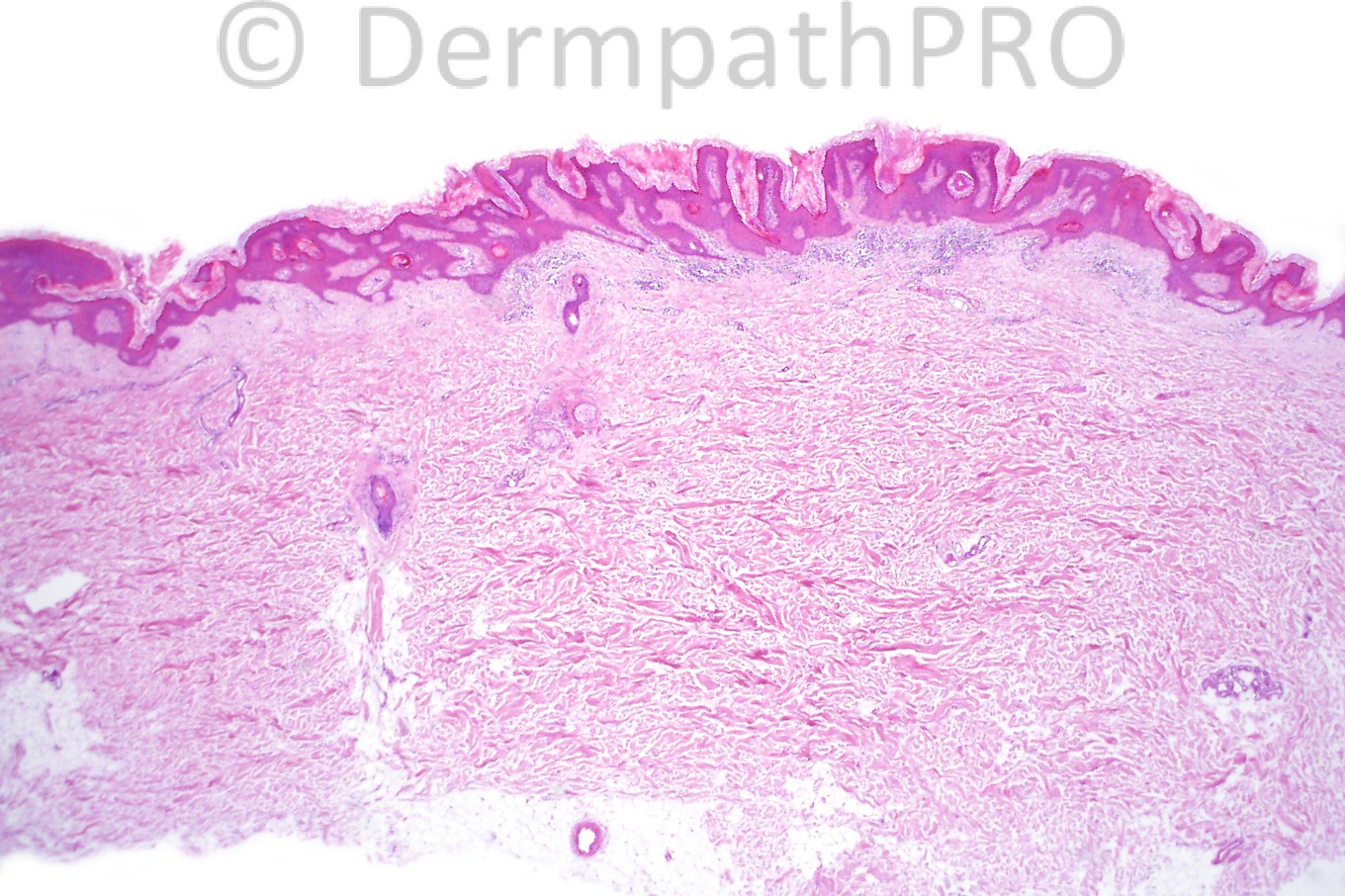
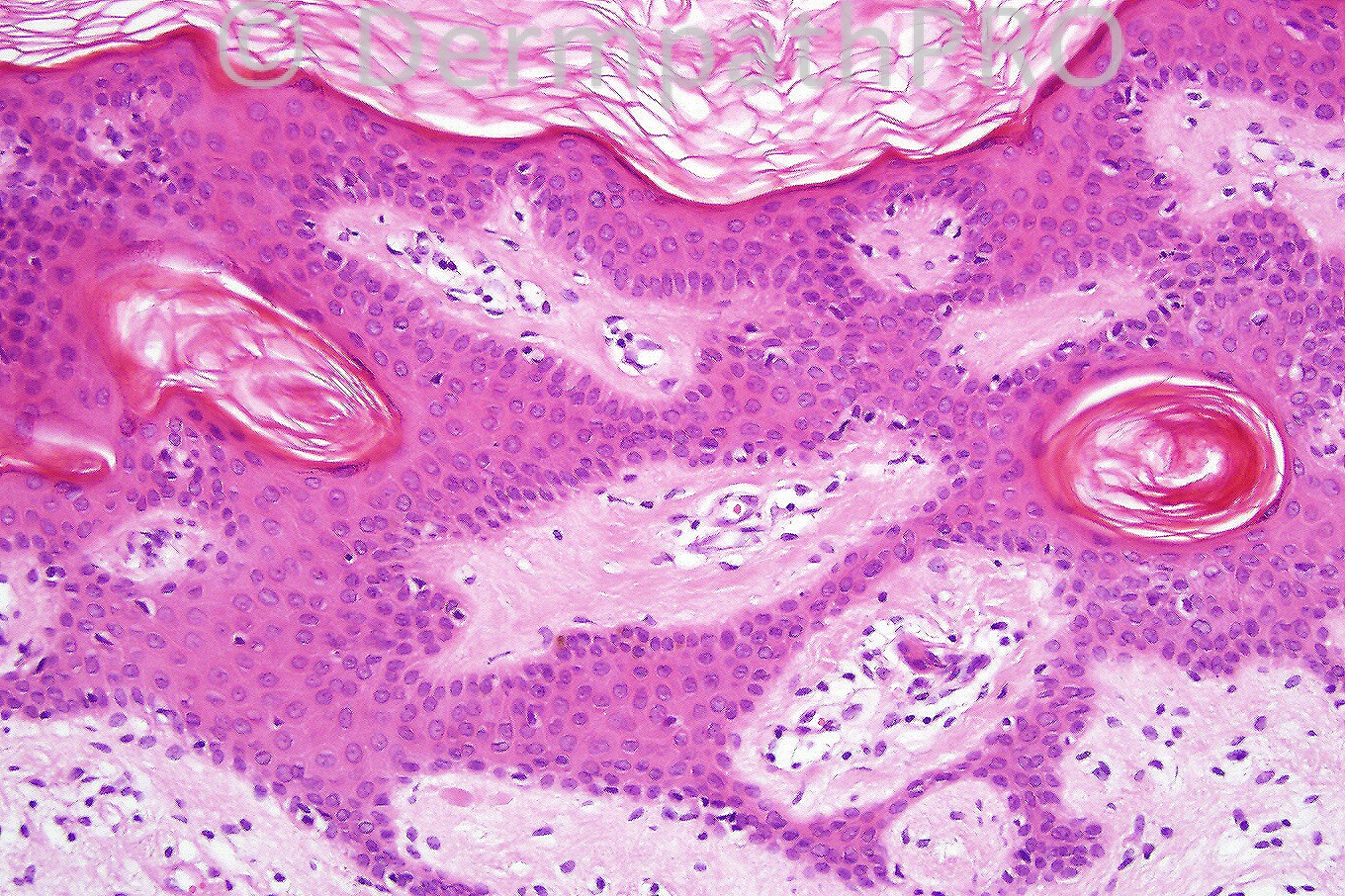
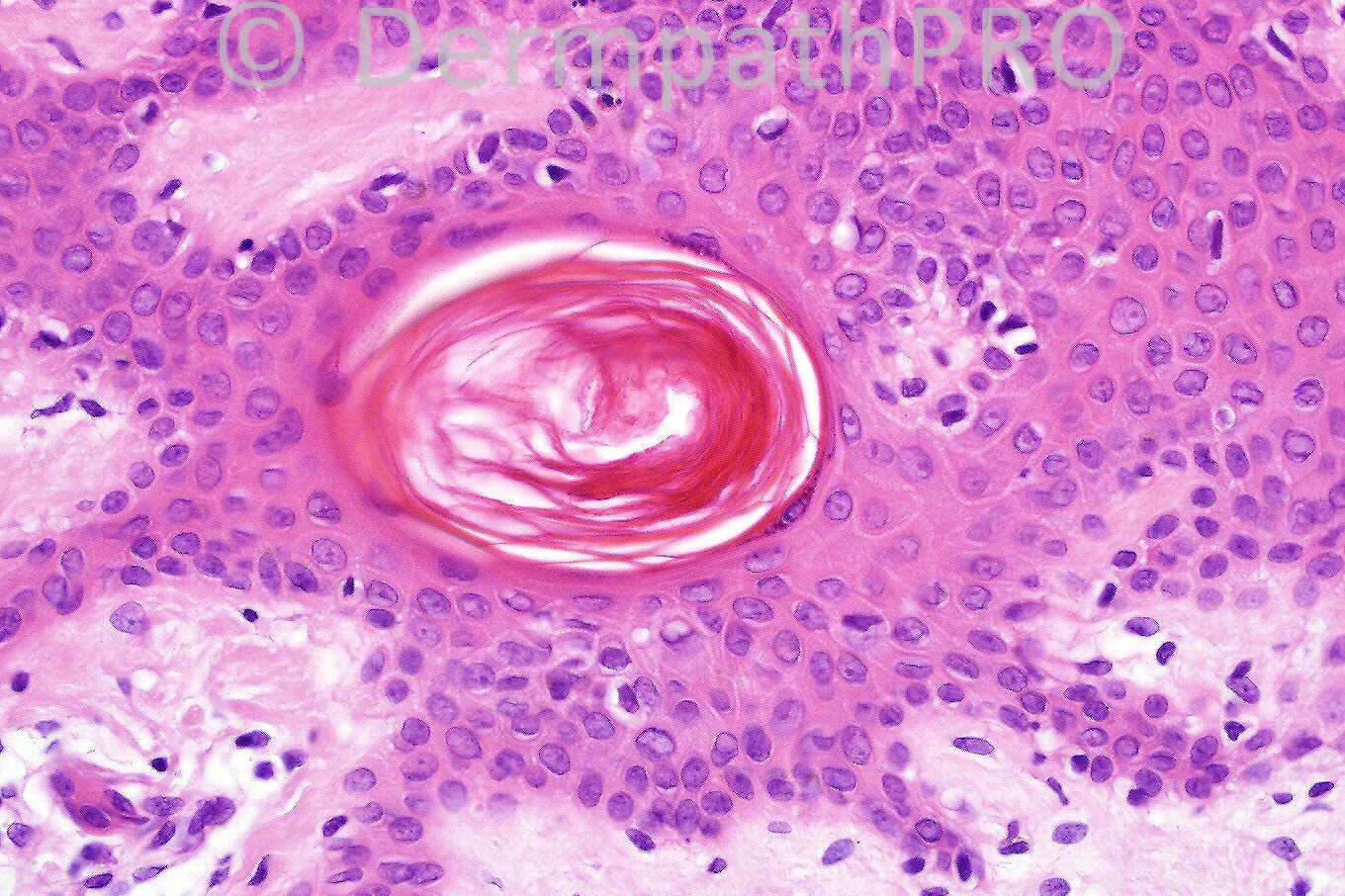
Male 6 years with a scaly, warty lesion on his arm.


User Feedback